Have you ever wondered how a tiny insect can sustain a massive bird of prey? The answer lies in the intricate web of energy flow within an ecosystem, beautifully visualized by the energy pyramid. This powerful tool helps us understand the interconnectedness of life and how energy moves through different trophic levels. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of energy pyramids, exploring how they function, their importance in ecological studies, and how to confidently answer practice worksheets.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Imagine a towering structure, with each level representing a distinct group of organisms. At the base lie the producers, the foundation of life, converting sunlight into energy. As we climb higher, we encounter herbivores, consuming plants, and then carnivores, feeding on herbivores. Each level represents a step in the energy flow, and as we ascend, the amount of energy available decreases, creating the pyramid shape.
Understanding the Energy Pyramid: A Closer Look
Producers: The Foundation of Life
At the base of the energy pyramid sit the producers, also known as autotrophs. These remarkable organisms, like plants and algae, harness the power of sunlight through photosynthesis, converting it into chemical energy stored in sugars. The energy stored in their bodies forms the primary source for all other organisms within the ecosystem. Think of them as the architects of life, building the foundation upon which the entire structure rests.
Consumers: The Energy Consumers
Moving up the pyramid, we encounter consumers, also known as heterotrophs. These organisms rely on other organisms for their energy, unable to produce their own.
- Primary consumers, also known as herbivores, graze on plants, directly deriving their energy from producers.
- Secondary consumers, primarily carnivores, prey on herbivores, obtaining energy from the herbivores they consume.
- Tertiary consumers, the apex predators, feed on secondary consumers, sitting at the top of the food chain, their existence supported by the energy flow from the base.
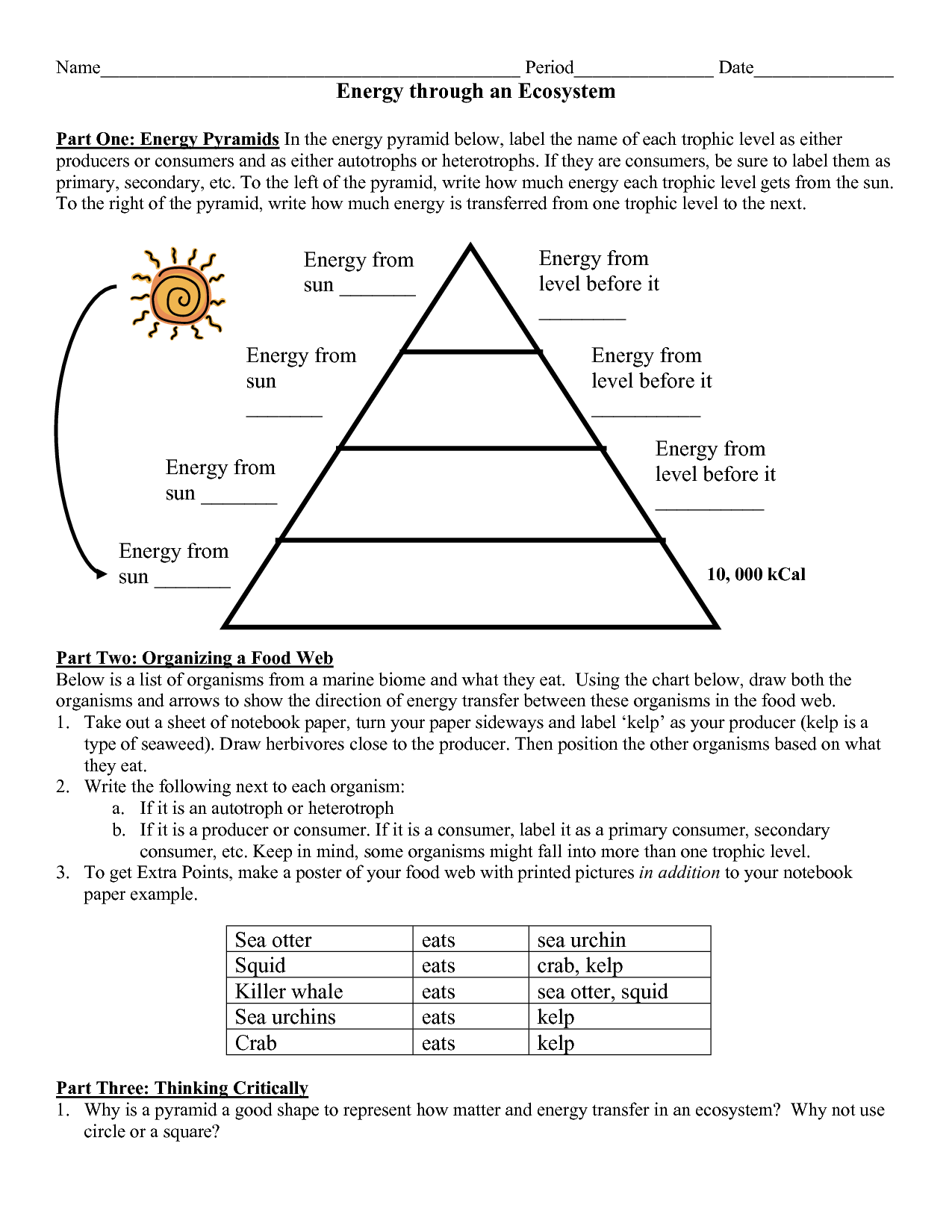
Image: www.worksheeto.com
The 10% Rule: Energy Loss in the Food Web
One crucial concept to understand is the 10% rule. It states that only about 10% of the energy stored in one trophic level is transferred to the next. This energy loss primarily occurs through various biological processes, such as respiration, movement, and heat generation. As we move up the pyramid, the amount of energy available decreases significantly, limiting the number of organisms that can be supported at higher levels.
Decomposers: The Silent Recyclers
While the pyramid focuses on energy flow through consumption, the role of decomposers cannot be overlooked. These unsung heroes, like bacteria and fungi, break down dead organisms and waste products, returning nutrients to the soil, completing the cycle. Decomposers play a vital role in nutrient recycling, ensuring that the ecosystem remains balanced.
Energy Pyramid Practice Worksheets: Mastering the Concepts
Now that we understand the intricate workings of the energy pyramid, let’s tackle those practice worksheets! These worksheets, often used in biology classes, test our understanding of energy flow in ecosystems. Let’s examine some common questions and their answer key:
1. Identifying Trophic Levels
One common practice involves identifying the trophic levels of different organisms. For instance, a question might ask:
“Identify the trophic level of a rabbit in a grassland ecosystem.”
The answer would be primary consumer, as rabbits feed on plants, placing them at the herbivore level.
2. Understanding Energy Transfer
Another type of question might involve calculating energy transfer between levels. A question could ask: “If a producer has 1000 calories of energy, how much energy is available to a secondary consumer?”
To solve this, we apply the 10% rule.
- Primary consumer: 1000 calories * 10% = 100 calories
- Secondary consumer: 100 calories * 10% = 10 calories
Therefore, 10 calories are available to the secondary consumer.
3. Analyzing Food Webs
Practice worksheets often feature food web diagrams, showcasing multiple interconnected food chains. A question could ask: “Identify the top predator in the following food web.” By carefully examining the diagram, we can pinpoint the organism at the highest trophic level, consuming other predators, to answer the question correctly.
4. Constructing Energy Pyramids
Some worksheets might challenge students to construct energy pyramids themselves. They provide data on the biomass or energy content of different trophic levels. Students must then arrange the levels in order, ensuring that the pyramid represents the energy flow accurately.
Mastering the Energy Pyramid: Real-World Applications
The knowledge gained from studying energy pyramids extends far beyond the classroom. It finds practical applications in various fields, influencing our understanding of:
1. Conservation Efforts
Understanding energy flow helps us understand how human activities like fishing or logging can impact ecosystems. By understanding the energy pyramid, we can implement sustainable practices, ensuring the long-term health of ecosystems and the species that inhabit them.
2. Agricultural Practices
The energy pyramid helps optimize agricultural practices, maximizing the energy efficiency of crops. By understanding the energy transfer from producers to consumers, we can design efficient farming systems that minimize energy loss and maximize food production.
3. Food Security
Energy pyramids provide insights into food security, assisting in developing strategies to ensure everyone has access to nutritious food. As our planet’s population continues to grow, understanding energy flow within food chains is crucial to sustainable food production.
Energy Pyramid Practice Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion
Mastering the energy pyramid practice worksheet is not just about passing a test but about appreciating the complex and interconnected nature of ecosystems. By understanding this fundamental concept, we gain a deeper understanding of the delicate balance of life on Earth. So, dive into those practice worksheets, unlock the secrets of energy flow, and become an energy pyramid master!






