Imagine a person confined to their bed, their movements limited by a debilitating injury or illness. This is the harsh reality for countless individuals struggling with impaired physical mobility. It can feel like a prison, robbing them of their freedom, independence, and joy. But amidst this struggle, a beacon of hope shines – skilled nurses who tirelessly work to restore mobility, empowering their patients to reclaim their lives.
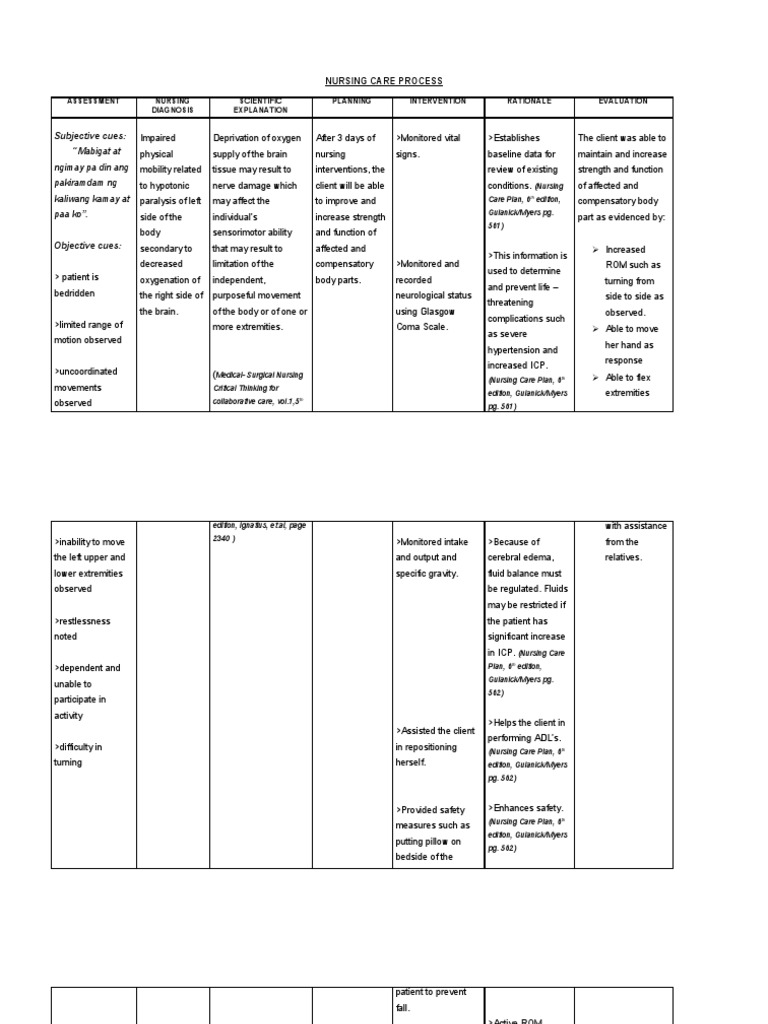
Image: www.scribd.com
This article delves into the world of nursing interventions for impaired physical mobility, exploring the diverse strategies nurses employ to help patients regain their strength, function, and independence. We’ll uncover the underlying principles, discuss the latest innovations, and offer insights from seasoned healthcare professionals. So, let’s begin this journey towards a brighter future for those affected by mobility challenges.
Understanding Impaired Physical Mobility: A Closer Look
Impaired physical mobility refers to a limitation in the ability to independently move and perform daily activities. This limitation can arise from a myriad of causes, including:
- Musculoskeletal conditions: Arthritis, osteoporosis, fractures, and muscular dystrophy can significantly hamper movement.
- Neurological disorders: Stroke, spinal cord injuries, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis can affect muscle control and coordination.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Heart failure and peripheral artery disease can limit endurance and stamina.
- Post-surgical recovery: Following surgery, patients may experience pain, weakness, and limited range of motion.
- Aging: As we age, our muscles naturally lose mass and strength, often leading to decreased mobility.
Impaired physical mobility can have a profound impact on a person’s quality of life, affecting their ability to perform tasks like walking, dressing, bathing, and even simply getting out of bed. It can also lead to social isolation, depression, and anxiety.
Nursing Interventions: A Multifaceted Approach
Nursing interventions for impaired physical mobility are designed to address the individual’s specific needs and goals. These interventions are tailored to each patient’s unique physical status, medical history, and lifestyle. Nurses work closely with patients to develop a personalized plan, often collaborating with physical therapists, occupational therapists, and other healthcare professionals.
Let’s explore some of the most effective nursing interventions:
1. Assessment and Evaluation: The Foundation of Care
Before any intervention can be implemented, a thorough assessment is crucial. Nurses meticulously evaluate the patient’s current mobility status, pain levels, functional limitations, and any underlying medical factors. This comprehensive assessment provides the foundational knowledge needed to craft effective and targeted interventions.

Image: nandadiagnoses.com
2. Passive Range of Motion (PROM): Maintaining Joint Flexibility
If a patient is unable to move their joints independently, nurses perform passive range of motion exercises to prevent stiffness, contractures, and muscle atrophy. This involves gently moving the affected joints through their full range of motion, ensuring optimal joint health and function.
3. Active Range of Motion (AROM): Strengthening Muscles and Joints
As patients gradually regain strength, nurses encourage active range of motion exercises. These exercises require the patient to actively move their joints, engaging their own muscles to improve flexibility, strength, and coordination.
4. Ambulation Assistance: Rebuilding Independence
From walking aids like canes and walkers to specialized devices and caregiver support, nurses guide patients through a carefully planned ambulation program. This program helps them safely rediscover the joy of walking, promoting physical independence and improving overall well-being.
5. Transfer Techniques: Moving With Ease and Safety
Transferring from bed to chair or wheelchair can be a daunting task for individuals with mobility limitations. Nurses are adept at using safe and efficient transfer techniques, ensuring both patient safety and dignity. From specialized lifts to manual handling techniques, nurses create a comfortable and supportive environment for movement.
6. Positioning: Alleviating Pressure and Promoting Comfort
Proper positioning is vital in preventing pressure ulcers, promoting lung expansion, and ensuring optimal circulation. Nurses are trained in various positioning techniques, including side-lying, supine, and prone positioning, to optimize comfort, reduce pressure, and enhance overall well-being.
7. Pain Management: Enhancing Comfort and Function
Pain can significantly hinder movement. Nurses use a variety of pain management strategies, including medication, heat therapy, and massage, to effectively alleviate pain and allow patients to participate in rehabilitation exercises.
8. Skin Care: Preventing Pressure Ulcers
Impaired mobility increases the risk of pressure ulcers. Nurses meticulously assess skin condition, implement pressure-relieving measures, and educate patients on proper skincare practices to prevent these debilitating wounds.
9. Promoting Mobility:
Encouraging patients to assist with their transfers, to actively participate in range of motion exercises, and to move around as much as their capabilities allow promotes independent mobility. They provide encouragement, positive reinforcement, and guidance to help patients achieve their goals.
10. Education and Empowerment: Working Together
Nurses play a vital role in educating patients and their families about mobility challenges, available resources, and self-care strategies. Empowering them with knowledge and tools for managing their condition helps maintain independence and fosters a sense of control.
Expert Insights: The Power of Collaboration
“Our role as nurses goes beyond simply performing tasks,” shares Mary, a seasoned nurse with decades of experience in rehabilitation. “We are trusted advisors, educators, and advocates for our patients. We work collaboratively with the entire healthcare team to ensure that patients receive the most effective and compassionate care.”
She emphasizes the importance of family involvement, saying, “Families are instrumental in helping their loved ones reach their full potential. We empower them with the knowledge and tools to provide ongoing support, encouraging ongoing rehabilitation and helping their loved ones stay active.”
Actionable Tips for Promoting Mobility
You can empower yourself to stay active and maintain mobility by adopting these simple steps:
- Engage in regular physical activity: Even light exercise like walking, swimming, or yoga can strengthen muscles and improve balance.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity increases stress on joints and can impair mobility.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains: Nourishing your body with essential nutrients promotes muscle function and overall health.
- Consult with your doctor: If you experience any pain or limitations, seek medical guidance promptly to identify the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Nursing Interventions For Impaired Physical Mobility
Conclusion: A Journey Towards Independence
Nursing interventions for impaired physical mobility play a critical role in empowering individuals to regain their independence and enjoy a fulfilling life. From meticulous assessments to implementing tailored care plans, nurses are dedicated to helping patients overcome mobility challenges and reach their full potential.
By understanding the diverse interventions available, encouraging family involvement, and adopting healthy habits, you can contribute to fostering a positive and supportive environment for individuals facing mobility limitations. Remember, the journey towards independence starts with a commitment to progress, and with the right support and guidance, a brighter future awaits.






