I remember the first time I encountered a mechanical engineering drawing. It was a jumble of lines, circles, and strange symbols that left me utterly confused. What did it all mean? How could anyone understand such a complex visual language? The truth is, mechanical engineering drawings are more than just lines and shapes; they are a powerful form of communication, carrying the blueprints for complex machines and intricate systems. But only if you know how to read them.
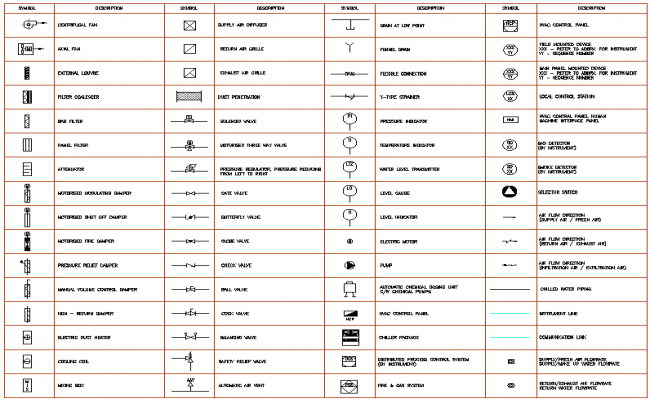
Image: mungfali.com
This article aims to demystify the world of mechanical engineering drawing symbols and meanings. We’ll explore the key symbols, understand their purpose, and learn how to interpret them effectively. Whether you’re a student just starting out or a seasoned professional, this guide will provide you with the tools you need to decipher these essential blueprints of the engineering world.
Understanding the Language of Mechanical Engineering Drawings
Mechanical engineering drawings are the foundation of any design process. They are the visual representations that translate an idea from the engineer’s mind to a tangible object. These drawings provide precise instructions for the manufacture, assembly, and operation of machines, components, and structures. To comprehend these drawings, it’s crucial to understand the symbols used within them.
These symbols are not arbitrary; they have been standardized to ensure clarity and consistency in communication across the engineering industry. Each symbol represents a specific feature, dimension, or manufacturing instruction, allowing engineers to communicate ideas with precision and avoid misinterpretations. This standardization leads to greater efficiency and reduces the potential for costly errors during production.
Types of Mechanical Engineering Drawing Symbols
Mechanical engineering drawing symbols are divided into categories representing different aspects of the design. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Dimensioning Symbols
These symbols indicate the size and shape of objects. They include:
- Dimension lines: Thin lines with arrowheads at each end, indicating the distance between two points.
- Extension lines: Thin lines extending from the object’s features to the dimension line.
- Leaders: Lines connecting text to a specific feature on the drawing.
- Diameter symbol (Ø): Used to denote the diameter of circles and arcs.
- Radius symbol (R): Indicates the radius of a circle or arc.

Image: www.pinterest.com.au
2. Geometric Shapes and Features
Represent standard geometric shapes and features used in engineering designs. They include:
- Square (□): Indicates a square shape.
- Circle (○): Represents a circle.
- Triangle (△): Indicates a triangle.
- Arc (⏞): Represents a portion of a circle’s circumference.
- Tangent (⏊): Used to denote a line that touches a curve at exactly one point.
3. Material Symbols
These symbols are used to specify the materials used in the design process and include:
- Steel (S): Represents steel for construction.
- Aluminum (Al): Denotes aluminum.
- Copper (Cu): Symbol for copper.
- Plastic (P): Specifies plastic materials.
- Wood (W): Represents wood.
4. Manufacturing and Assembly Symbols
These symbols provide instructions on how to manufacture and assemble the objects. They include:
- Drilling (⊟): Represents the drilling operation.
- Tapping (⊟): Indicates the tapping operation.
- Welding (⏓): Used to denote welding.
- Riveting (⏭): Represents riveting.
5. Tolerances and Fits
These symbols indicate the acceptable variations in size and shape. They include:
- Plus/minus symbol (+/-): Indicates the tolerance range.
- Clearance (C): Represents the space between two mating parts.
- Interference (I): Denotes the overlap between two mating parts.
Learning and Using Mechanical Drawing Symbols
The best way to learn and understand mechanical engineering drawing symbols is through practice. Here are some tips you can follow:
- Start with basic symbols: Begin by familiarizing yourself with the most common symbols used in drawings. There are plenty of resources online and in textbooks that provide comprehensive lists with explanations.
- Analyze real drawings: Try to interpret real mechanical engineering drawings as much as possible. You can find numerous examples online or in engineering books. Start with simple drawings and gradually move towards more complex ones.
- Use reference materials: Keep a copy of standard symbol tables handy for reference during your practice sessions. Many engineering resources offer detailed guides with explanations and illustrations of the symbols.
- Practice drawing yourself: Drawing simple components and shapes using the symbols you’ve learned can solidify your understanding. This hands-on practice helps you develop a more intuitive grasp of the meaning behind each symbol.
Remember, mastering mechanical drawing symbols is an ongoing process. As you work on more complex designs, you’ll encounter new symbols, and your understanding of these visual tools will continue to grow. With consistent practice and a clear understanding of their purpose, you can decipher and interpret even the most intricate mechanical drawings.
Expert Advice: Tips for Mastering Mechanical Engineering Drawings
My experience with mechanical drawings has taught me that the key to effectively using these blueprints is not just memorizing symbols but understanding the context in which they are used. Here’s my advice:
- Pay Attention to Context: While memorizing symbols is important, it’s equally crucial to consider the context in which they are used. The location of a symbol within a drawing, along with the surrounding information and dimensions, provides crucial context for understanding its meaning.
- Don’t Overlook the Title Block: The title block is often overlooked but contains valuable information, including the title of the drawing, the project number, the date of creation, and the creator’s name. All of which can add layers of context to the drawing.
- Practice Drawing: Creating your own drawings, even if they are simple, can be a powerful learning tool. By drawing, you begin to grasp the relationship between the symbols and the 3D object they represent.
- Utilize Software: CAD software is becoming increasingly popular in the engineering field. Learning to use these programs to create and interpret mechanical drawings can significantly enhance your understanding and efficiency.
FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about mechanical engineering drawing symbols:
Q: Where can I find a comprehensive list of mechanical engineering symbols and their meanings?
A: Numerous resources provide detailed information about mechanical engineering drawing symbols and their meanings. Popular options include:
- Engineering textbooks: Check out introductory mechanical engineering textbooks; they often feature dedicated chapters on drafting and drawing symbols.
- Online databases: Many engineering websites offer free or paid databases that contain extensive information on various symbols.
- Technical standards organizations: Organizations like ASME and ISO publish detailed standards for drafting and drawing symbols.
Q: Are standardized drawing symbols universal across all engineering disciplines?
A: While many standardized symbols are widely recognized across different engineering disciplines, slight variations may exist depending on the specific industry or company’s internal standards. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the specific symbols used within your industry or workplace to avoid misinterpretations.
Q: How do I interpret drawings involving multiple views?
A: Mechanical engineering drawings often utilize multiple views to provide a complete picture of the object. These views typically include a front view, side view, and top view. By understanding the relationship between these different views, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the 3D object represented in the drawing.
Q: How important is it to understand mechanical engineering drawings in today’s technologically advanced world?
A: Despite the rise of digital modeling and simulation tools, understanding mechanical engineering drawings remains essential. These drawings serve as communication tools, providing clear and concise instructions for manufacturing, assembly, and material selection. Therefore, even in a world of digital technology, the ability to read and interpret mechanical drawings remains a valuable skill.
Mechanical Engineering Drawing Symbols And Meanings Pdf
Conclusion
Mechanical engineering drawings are the heartbeat of the engineering world, and understanding their language is crucial for anyone involved in design, manufacturing, or assembly. This article has provided a comprehensive guide to the symbols used in these drawings, emphasizing the importance of context, practice, and ongoing learning. It’s a skill worth cultivating, as it can unlock the secrets hidden behind these visual blueprints, propelling your career and projects forward with greater clarity and efficiency.
Are you interested in learning more about specific drawing symbols or delving deeper into the world of mechanical engineering drawings? Let me know in the comments below, and I’ll be happy to discuss further!






