Have you ever wondered why some solutions, like vinegar or lemon juice, tingle your taste buds while others, like distilled water, feel bland? The answer lies in the world of acids, specifically weak acids – those that don’t fully dissociate in water, leaving a symphony of ions and undissociated molecules. Understanding how these weak acids behave, particularly their dissociation constant (Ka), is crucial in fields ranging from chemistry and biology to medicine and environmental science.
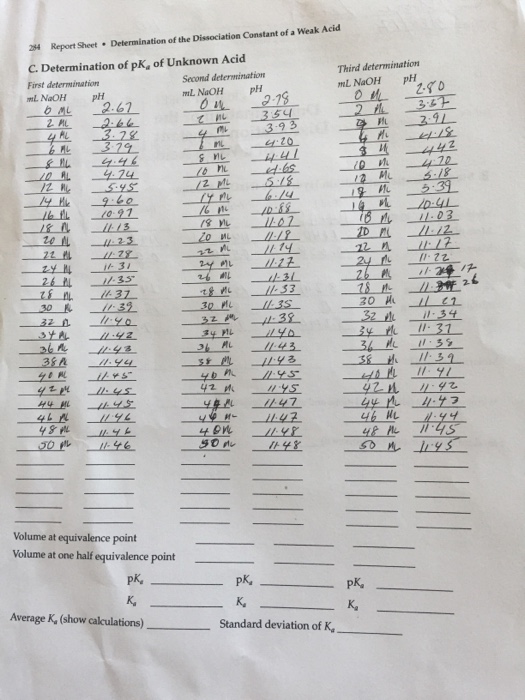
Image: www.chegg.com
But what exactly is Ka? It’s a measure of how much a weak acid will dissociate in water, revealing the strength or weakness of that acid. The higher the Ka value, the stronger the acid and the more it releases hydrogen ions (H+). In this article, we’ll dive deep into the determination of the dissociation constant of a weak acid, exploring different methods, practical applications, and the profound impact this knowledge has on our lives.
Delving into the Dissociation Constant (Ka): A Journey into the World of Weak Acids
Imagine a bustling party with people constantly moving in and out. Some stay put, while others mingle and form new connections. Weak acids are like this party – they don’t fully dissolve in water, leaving a dynamic mixture of undissociated molecules and ions. The dissociation constant (Ka) is like a snapshot of this scene, revealing the ratio between the concentration of ions and undissociated molecules.
The Foundations: Equilibrium and the Law of Mass Action
To truly grasp Ka, we need to understand the concept of chemical equilibrium. In the case of weak acids, equilibrium is achieved when the rate of dissociation (acid breaking down into ions) equals the rate of association (ions recombining to form the undissociated acid). This state of balance is governed by the Law of Mass Action, which tells us that the ratio of products to reactants is constant at equilibrium.
Calculating Ka: Quantifying the Dissociation of Weak Acids
The dissociation constant (Ka) is calculated using a simple formula:
Ka = ([H+][A-])/[HA]
Where:
- [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions
- [A-] is the concentration of the conjugate base
- [HA] is the concentration of the undissociated weak acid
This formula neatly captures the ratio of products (ions) to reactants (undissociated acid) at equilibrium, giving us a quantitative measure of the acid’s strength.

Image: www.youtube.com
A Tale of Two Methods: Determining Ka in the Lab
There are two common approaches used to experimentally determine Ka:
-
Conductivity Method: This technique relies on the fact that ions conduct electricity. By measuring the conductivity of a weak acid solution at different concentrations, we can deduce the concentration of ions and ultimately calculate Ka.
-
pH Method: Using a pH meter, we can measure the solution’s pH, which tells us the concentration of hydrogen ions. Applying the formula for Ka, we can then calculate the dissociation constant.
Beyond the Equation: Unveiling the Importance of Ka
Ka is not just a numerical value tucked away in textbooks. It has tangible real-world implications:
-
Buffer Solutions: Ka plays a crucial role in creating buffer solutions, which resist changes in pH. This is essential in biological systems, where maintaining a constant pH is vital for enzymatic activity and overall function.
-
Acid-Base Titrations: Ka is a key factor in determining the endpoint of acid-base titrations, which are used to analyze and quantify solutions.
-
Pharmaceutical Applications: In the pharmaceutical industry, Ka is essential for optimizing the formulation of drugs, ensuring their stability and efficacy.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Ka is critical for environmental monitoring, helping us understand the fate and impact of pollutants in natural ecosystems.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips: Mastering the Dissociation Constant
To truly understand and utilize Ka effectively, here are some valuable insights from experts:
-
Visualize the Dissociation: Instead of just looking at formulas, visualize the dissociation process of a weak acid. Imagine molecules breaking down into ions and understand how factors like concentration and temperature can affect the equilibrium.
-
Practice, Practice, Practice: Solving practice problems involving Ka is key to building confidence and solidifying your understanding.
-
Embrace the Resources: There are numerous online resources and textbooks that can offer additional insights and explanations.
Determination Of The Dissociation Constant Of A Weak Acid
In Conclusion: Empowering You with Knowledge
Understanding the concept of the dissociation constant (Ka) empowers you to delve deeper into the fascinating world of weak acids. From its profound implications in biological systems to its diverse applications in various fields, Ka is a crucial concept that connects chemistry to our everyday lives. By embracing knowledge and utilizing the insights shared in this article, you’re not only expanding your scientific horizons but also equipping yourself with valuable tools for future explorations. So, go forth, delve into the world of Ka, and unlock the secrets of weak acids!






