Remember that time your car’s headlights randomly stopped working? You frantically searched for the problem, unsure of what could be wrong. Finally, you discovered a blown fuse, a simple fix that had you back on the road in no time. That’s the power of understanding your car’s fuse box. For 2011 GMC Acadia owners, the fuse box is a vital component to keeping your vehicle running smoothly.
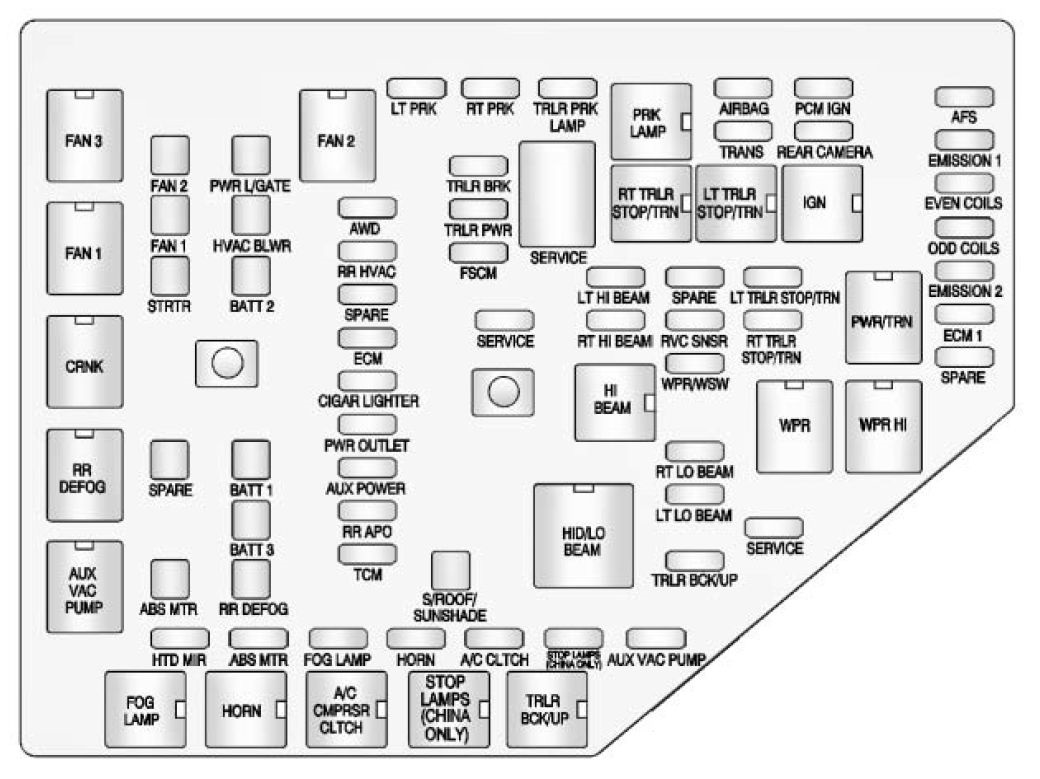
Image: sicherungskasten-auto.com
Knowing where the fuse box is located and how to use a fuse box diagram is essential for any car owner. It can be the difference between being stranded on the side of the road or solving a minor electrical problem yourself. In this guide, we’ll take a deep dive into the 2011 GMC Acadia fuse box diagram, providing you with all the information you need to navigate the electrical system of your vehicle.
Understanding the Fuse Box
The fuse box is the central hub for your car’s electrical system. It contains a series of fuses and relays, which protect your vehicle’s electrical circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. Each fuse is designed to melt and break the circuit if too much current flows through it. This prevents damage to more expensive components like your engine, radio, or headlights.
The 2011 GMC Acadia features two primary fuse box locations: the underhood fuse box and the passenger compartment fuse box. The underhood fuse box, also known as the power distribution center, is located in the engine bay near the battery. It houses fuses and relays for essential components such as the engine, lighting, and power accessories. On the other hand, the passenger compartment fuse box, located in the driver’s side footwell, contains fuses for components like the audio system, climate control, and power outlets.
Deciphering the 2011 GMC Acadia Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram is a visual representation of the fuse box. It displays each fuse’s location, amperage rating, and the components it protects. Understanding the diagram is key to diagnosing and solving electrical issues quickly. Here’s how to read the diagram effectively:
Locate the Diagram
Your 2011 GMC Acadia fuse box diagram can be found:
- Inside the fuse box lid: Many manufacturers include a diagram right on the lid of the fuse box, making it readily accessible. Look for a small sticker or printed diagram.
- In your owner’s manual: The owner’s manual should contain a detailed fuse box diagram with explanations for each fuse.
- Online resources: Numerous websites provide free and downloadable fuse box diagrams for specific car models, including the 2011 GMC Acadia. You can search online for “2011 GMC Acadia fuse box diagram” for several options.
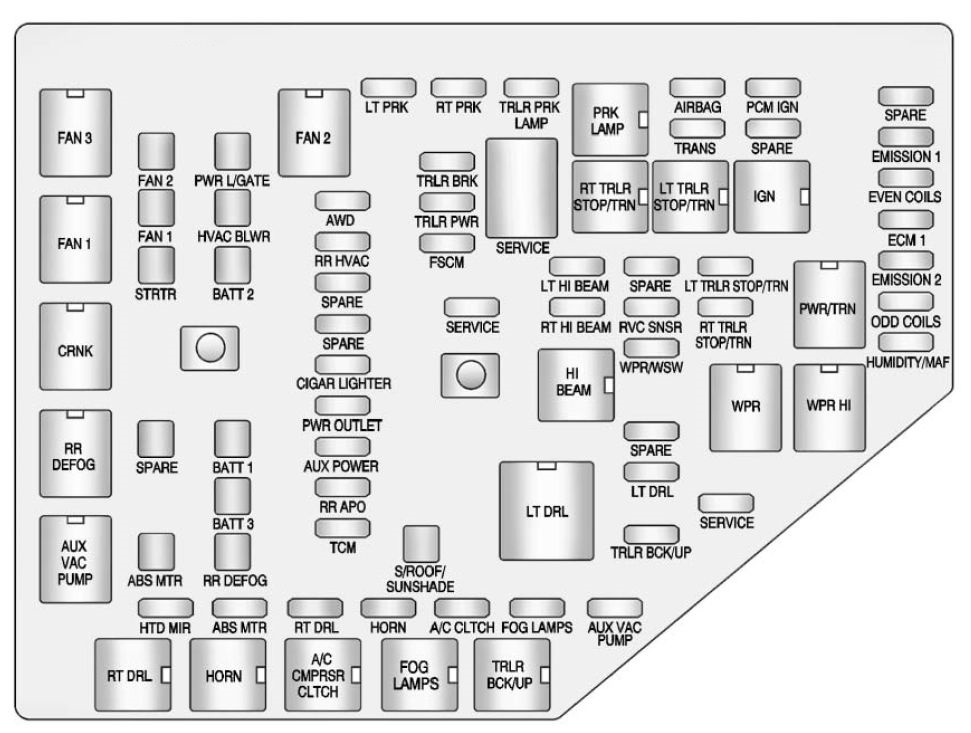
Image: www.carknowledge.info
Understand the Components
The diagram will use standard icons and symbols to represent different electrical components. For instance:
- Fuse: A small circle with a number representing the fuse position.
- Relay: A square with a coil inside, often labeled with the relay’s purpose.
- Component: An icon representing the component, such as a headlight, radio, or power outlet.
Identify Fuse Amperage
Each fuse in the diagram will have a number representing its position in the box. The amperage rating is usually listed next to the fuse number. This information tells you the maximum amount of current that fuse can handle before it blows. Choose a replacement fuse with the same amperage rating as the blown fuse to avoid overloading the circuit and causing additional damage.
Troubleshooting with the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram is an invaluable tool when troubleshooting electrical problems in your 2011 GMC Acadia. Here’s how to use it effectively:
- Identify the malfunctioning component: Determine which part of the vehicle is not working, for example, headlights, radio, or power windows.
- Locate the corresponding fuse: Refer to the diagram to find the fuse responsible for that component.
- Inspect the fuse: Carefully inspect the fuse to see if it’s blown. A blown fuse will have a broken wire inside, usually appearing blackened or melted.
- Replace the blown fuse: Use a fuse puller to remove the blown fuse and replace it with a new one of the same amperage rating.
- Check the component: Try the component again to see if it is working.
- Investigate further: If the component is still not working, the problem may be beyond a blown fuse. Refer to your owner’s manual or a professional mechanic for further diagnosis.
Important Fuse Box Tips and Expert Advice
While the fuse box diagram is a helpful tool, keep these tips in mind for optimal use:
- Always use a fuse puller: Do not use pliers or anything other than a specialized fuse puller to remove fuses. Using the wrong tools can damage the fuse.
- Always use fuses of the correct amperage: Replacing a blown fuse with one of higher amperage can lead to dangerous overheating and damage to electrical components. Use the same amperage as the original fuse or consult your owner’s manual.
- Never replace a blown fuse with a wire or other makeshift solution: This can lead to electrical fires and severe damage. A blown fuse is a signal that a circuit is overloaded or has a short, so it indicates a problem that needs to be addressed.
- Don’t leave a blown fuse in the box: A blown fuse may look like it’s fine but could have a partial break, which may still overload the circuit. Replace any blown fuse with a new one.
If you are uncomfortable working on your car’s electrical system, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic. They have the knowledge, tools, and experience to diagnose and repair any electrical issues safely and efficiently.
FAQ
Q: What does a blown fuse look like?
If a fuse has blown, you’ll see a broken wire inside. The fuse may appear blackened or melted.
Q: Where can I find replacement fuses?
You can usually find replacement fuses at most auto parts stores, hardware stores, or online retailers.
Q: What is the difference between a fuse and a relay?
A fuse is designed to melt and break a circuit when it becomes overloaded. A relay is an electrically operated switch that can control a high-current circuit using a low-current signal. Relays are often used to turn on components like headlights, horns, or fans.
Q: What should I do if a fuse keeps blowing?
If a fuse keeps blowing, there is likely a problem with the circuit it protects. Look for a short circuit, a loose wire, or a faulty component that is drawing too much power. Consult a professional mechanic if you’re unable to identify the problem.
Q: Can I use a fuse with a higher amperage to replace a blown fuse?
No, using a fuse with a higher amperage can lead to overheating and damage to electrical components. It is important to use the same amperage as the original fuse.
2011 Gmc Acadia Fuse Box Diagram
Conclusion
Understanding your 2011 GMC Acadia fuse box diagram is crucial for any car owner. By knowing the location and purpose of each fuse, you can quickly diagnose and solve minor electrical problems, keeping your vehicle running smoothly. Remember, safety is paramount when working with car electrical systems. If you have any doubts, consult a qualified mechanic. Are you interested in learning more about automotive electrical systems? Tell us in the comments below!






