Imagine a silent, unassuming instrument, hidden away in a building’s infrastructure, diligently watching over the flow of air through its veins. This is the role of the mercury manometer, a crucial component in ensuring the smooth operation and safety of ventilation systems. While often overlooked, its subtle dance of mercury reveals vital information about the pressure within air ducts, a factor that directly affects air quality, comfort, and even health.
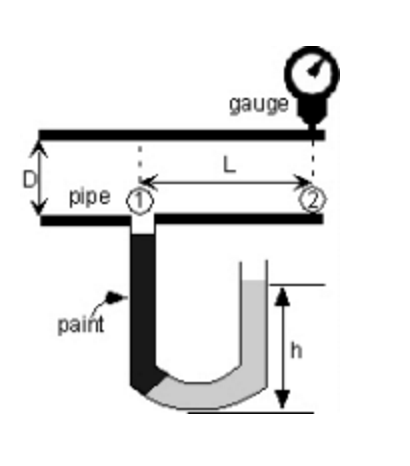
Image: www.chegg.com
This article delves into the world of mercury manometers, exploring their history, working principle, applications, and crucial role in various industries. We’ll uncover their significance in maintaining optimal airflow, detect potential problems, and ensure a healthy environment for those occupying the space. Join us as we unravel the fascinating story of this silent guardian of air quality.
A Glimpse into History: The Birth of a Pressure Gauge
The concept of measuring pressure dates back to ancient times, with rudimentary devices like the water clock demonstrating the relationship between pressure and height. However, the evolution of accurate pressure measurement took a significant leap forward in the 17th century with the invention of the barometer, attributed to Evangelista Torricelli. This device, utilizing mercury’s density and atmospheric pressure, paved the way for the development of manometers, specifically designed for measuring pressure differences.
The mercury manometer, as we know it today, emerged as a refinement of this principle, employing mercury’s high density and consistency to provide precise pressure readings. This simplicity and accuracy made it a valuable tool in various scientific and engineering applications, particularly in the realm of fluid mechanics and ventilation systems.
Understanding the Mechanics: How Mercury Tells the Tale
At the heart of the mercury manometer lies a simple yet ingenious principle. Two vertical tubes, connected at the bottom, are filled with mercury. The air duct is connected to one of these tubes, while the other is open to the atmosphere. The pressure difference between the air duct and the atmosphere pushes the mercury column in the open tube either higher or lower, depending on the pressure difference.
The height difference between the two mercury columns directly corresponds to the pressure difference. The higher the column in the open tube, the lower the pressure in the air duct and vice versa. This simple visual indication allows for immediate assessment of pressure conditions within the ventilation system.
Applications in the Real World: Keeping Your Air Healthy
The mercury manometer’s versatility extends beyond scientific laboratories into real-world applications, especially in the realm of ventilation systems. These applications include:
Image: www.coursehero.com
1. Monitoring Duct Pressure:
- Ensuring optimal airflow: A mercury manometer allows engineers and technicians to maintain the designated pressure difference across the air duct, ensuring efficient air distribution throughout the building. This is crucial for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures, removing stale air, and delivering fresh air to occupants.
- Detecting leaks: A drop in pressure might indicate leaks in the air duct, which can lead to energy loss and reduced efficiency. The manometer helps pinpoint these leaks for prompt repair.
2. Identifying Blockages:
- Troubleshooting airflow problems: A sudden rise in pressure could point towards a blockage in the air duct, restricting airflow. This can create discomfort for occupants, and the manometer helps to pinpoint the location of the blockage for quick removal.
3. Assessing Fan Performance:
- Evaluating fan efficiency: The mercury manometer measures the pressure difference created by the ventilation fan, providing insights into its performance. This data helps assess the fan’s ability to deliver the required air volume, allowing for timely maintenance or replacement.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Modern Alternatives to Mercury
While mercury manometers have served as vital tools for generations, concerns about mercury’s toxicity and environmental impact have led to the development of alternative pressure measurement methods. These include:
1. Digital Manometers:
- Electronic precision: Digital manometers utilize sensors to measure pressure and display the readings digitally. These devices offer high accuracy, ease of use, and often include data logging capabilities for long-term monitoring.
2. Water Manometers:
- Environmentally friendly: Unlike mercury, water is non-toxic and readily available, making water manometers a more environmentally friendly alternative. While less precise than mercury manometers, they are suitable for applications where accuracy is not paramount.
The Future of Pressure Measurement: Embracing Innovation
The field of pressure measurement continues to evolve, with advancements in sensor technology and data analysis driving the development of even more sophisticated devices. These innovations offer improved accuracy, automation, and remote monitoring capabilities, enabling more efficient and data-driven decision making in ventilation systems.
While the use of mercury manometers has declined due to safety and environmental concerns, their legacy continues to inspire the development of advanced pressure measurement solutions. As we move forward, it is crucial to continue exploring innovative solutions that improve efficiency, precision, and environmental sustainability in our pursuit of optimal air quality.
A Mercury Manometer Is Connected To An Air Duct
Final Thoughts: The Unseen Guardian of Air Quality
The mercury manometer may be an inconspicuous instrument, but its presence ensures the smooth operation and safety of ventilation systems. From monitoring air pressure to detecting leaks and blockages, it plays a vital role in maintaining healthy indoor environments. While modern alternatives offer advancements, the mercury manometer’s legacy continues to shape the future of pressure measurement, reminding us of the enduring importance of accurate and reliable tools that keep the air we breathe clean and comfortable.






